
Transformers, the unsung heroes of our electrical infrastructure, play a pivotal role in the seamless distribution of power. Among these, single-phase transformers stand out for their unique construction and efficient working mechanisms. Let’s delve into the intricacies of these transformers, exploring their construction and understanding the science behind their functionality.
1: Basics of Single Phase Transformer
1.1 Definition and Purpose
A single phase transformer is a vital component in the electrical ecosystem, designed to transfer electrical energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction. Understanding its purpose begins with grasping the fundamental concept of voltage transformation.
1.2 Primary and Secondary Windings of single phase transformer
At the heart of every single-phase transformer lie the primary and secondary windings. These coiled copper or silver conductors, wrapped around a silicon steel core, facilitate the transfer of electrical energy. The ratio of turns in these windings determines the voltage transformation for example 415 volts to 220 volts, making it a versatile tool in power and distribution systems.
2- Construction and Components
2.1 Silicon steel Core Material ( CRGO)
The core material of a single-phase transformer is crucial for its efficiency. Common materials include laminated iron core steel sheet, providing high magnetic permeability to enhance the transformer’s performance.
2.2 Windings and Insulation
The quality of the windings, coupled with effective insulation, ensures the durability and safety of the transformer. Manufacturers employ specialized materials to prevent short circuits and ensure a long operational life.
3- Transformer Oil and Cooling System
To maintain optimal temperature levels during operation, transformers are often filled with insulating oil. The cooling system, whether natural or forced, prevents overheating, safeguarding the transformer against potential damage.
4- Working Principle of single phase transformer
4.1 Magnetic Induction
The working principle of a single-phase transformer revolves around magnetic induction. When an alternating current flows through the primary winding, it creates a magnetic field, inducing a voltage in the secondary winding. This process enables the efficient transfer of electrical energy.
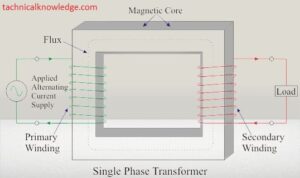
4.2 Voltage Transformation Process
The transformation of voltage occurs seamlessly, allowing the adjustment of voltage levels for specific applications. This feature makes single-phase transformers indispensable in various scenarios, from residential use to industrial applications.
5- Types of Single Phase Transformers
5.1 Distribution Transformers
These transformers are commonly found in residential areas, stepping down high-voltage power from utility lines to a level suitable for household consumption. They ensure a safe and reliable power supply to homes and small businesses.
5.2 Power Transformers
In industrial settings and power plants, power transformers handle higher voltage levels, facilitating the long-distance transmission of electricity. Their robust design and efficient performance contribute to the stability of large-scale power distribution networks.
6- Efficiency and Losses
6.1 Factors Affecting Efficiency
Several factors influence the efficiency of single-phase transformers, including core material quality, winding design, and the cooling system. Manufacturers continually strive to enhance these elements to improve overall efficiency.
6.2 Minimizing Losses in Transformers
Efforts to minimize losses in transformers involve advancements in design, materials, and operational practices. These innovations contribute to a more sustainable and energy-efficient electrical infrastructure.
7- Applications of Single-Phase Transformers
7.1 Residential Use
In households, single-phase transformers ensure a steady and safe power supply, supporting everyday activities. From lighting to powering electronic devices, these transformers play a crucial role in modern living.
7.2 Industrial Applications
Industries rely on single-phase transformers for various applications, including machinery operation and equipment powering. Their adaptability makes them essential in diverse industrial settings.

8- Maintenance Tips
8.1 Regular Inspection
Routine inspections are paramount to the longevity of single-phase transformers. Identifying and addressing issues promptly can prevent costly damages and downtime.
8.2 Addressing Common Issues
Understanding common issues, such as overheating or insulation breakdown, allows for proactive measures. Timely maintenance ensures the continuous and reliable operation of transformers.
9- Advancements in Transformer Technology
9.1 Smart Transformers
The integration of smart technology in transformers enables real-time monitoring and remote control. This innovation enhances efficiency, reduces downtime, and contributes to overall system reliability.
9.2 Sustainable Practices in Transformer Design
In response to environmental concerns, transformer manufacturers are adopting sustainable practices, from using eco-friendly materials to designing energy-efficient models. These initiatives align with global efforts toward a greener future.
10- Challenges in Single-Phase Transformers
10.1 Overloading Concerns
One of the challenges faced by single-phase transformers is the risk of overloading. Addressing this concern requires careful planning and periodic assessments to ensure transformers operate within safe limits.
10.2 Environmental Impact
As with any electrical equipment, transformers have an environmental impact. Manufacturers and operators are exploring ways to mitigate this impact through eco-friendly designs and responsible disposal practices.
11- Future Trends in Transformer Technology
11.1 Integration with Renewable Energy
The future sees single-phase transformers playing a crucial role in integrating renewable energy sources into the electrical grid. Their adaptability and efficiency make them key components in sustainable power systems.
11.2 Enhanced Efficiency Measures
Ongoing research and development focus on enhancing transformer efficiency. This includes exploring advanced materials, innovative designs, and predictive maintenance techniques for optimal performance.
12- Importance in Power Distribution
12.1 Role in Electrical Grids
Single-phase transformers form the backbone of electrical grids, ensuring the smooth flow and distribution of power. Their reliability is paramount to the stability of the entire grid infrastructure.
12.2 Supporting Sustainable Energy Practices
In the era of sustainability, single-phase transformers contribute to the adoption of clean energy practices. Their efficiency and adaptability support the integration of renewable sources, reducing reliance on conventional power generation.
13-Case Studies
Exploring real-world applications provides insights into the versatility of single-phase transformers. From small-scale residential installations to large industrial complexes, these case studies showcase the transformers’ effectiveness in diverse scenarios.
14-Safety Precautions
14.1 Compliance with Safety Standards
Adhering to established safety standards is non-negotiable in the realm of electrical equipment. Manufacturers, operators, and maintenance personnel must ensure that single-phase transformers meet and exceed safety regulations to guarantee secure operation.
15-Conclusion
In conclusion, the intricate world of single-phase transformers reveals their indispensable role in our daily lives and industrial landscapes. From the basic principles of magnetic induction to the cutting-edge technologies of smart transformers, these devices continue to evolve to meet the growing demands of our electrified society.
As we navigate the challenges of overloading concerns and environmental impact, the future of single-phase transformers holds promise. Their integration with renewable energy sources and continuous advancements in efficiency measures underscore their significance in shaping a sustainable and reliable power distribution infrastructure.
Understanding the construction, working principles, and applications of single-phase transformers provides a holistic view of their importance. As we embrace cleaner energy practices, these transformers stand as crucial components, supporting the transition towards a greener and more efficient electrical grid.
FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions
Are single-phase transformers only used in residential areas?
No, while they are common in residential areas, single-phase transformers also play a vital role in industrial applications, contributing to machinery operation and equipment powering.
How can I ensure the safety of a single-phase transformer during installation?
Follow the strict handling and installation guidelines provided by the manufacturer and ensure compliance with safety standards to guarantee secure operation.
What are the common maintenance issues with single-phase transformers?
Common issues include overheating and insulation breakdown. Regular inspections and timely addressing of issues can prevent costly damages.
How do smart transformers enhance efficiency?
Smart transformers integrate real-time monitoring and remote control capabilities, reducing downtime and contributing to overall system reliability.
What role do single-phase transformers play in supporting sustainable energy practices?
Single-phase transformers are crucial in integrating renewable energy sources into the electrical grid, supporting the adoption of clean energy practices.

Leave a Reply