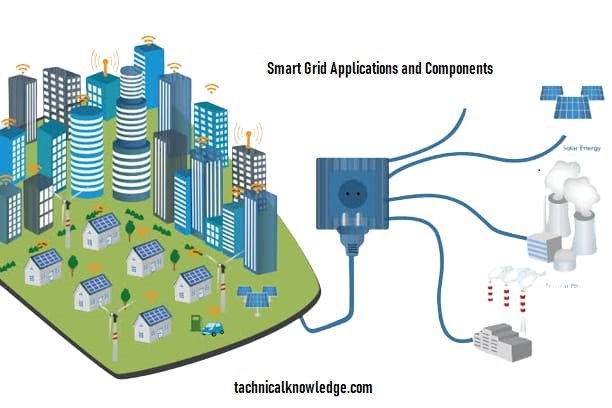
Smart Grid Applications and Components: The Future of Power Distribution
Introduction:
In recent years, the need for sustainable energy management has become increasingly urgent. The traditional power grid infrastructure has limitations in terms of reliability, efficiency, and adaptability, which have led to the development of the Smart Grid. The Smart Grid is an advanced technology that enables two-way communication between energy consumers and producers, making energy distribution more efficient, reliable, and sustainable. This article will explore the Smart Grid: Applications & Components, its potential benefits, and how it can shape the future of energy management.
What is a Smart Grid?
A smart grid is an advanced power distribution system that uses digital technology to monitor and control power flows, in real-time. It is a sophisticated network of connected hardware and software that works in concert to improve the efficiency and dependability of power delivery. This covers a wide range of technologies, such as home automation gadgets, energy storage systems, electric vehicles, and renewable energy sources like solar and wind power.

Applications of the Smart Grid
The smart grid has a wide range of applications, including:
1. Renewable Energy Integration
Integrating renewable energy sources into the power grid is one of the smart grid’s greatest benefits. With the popularity of solar and wind energy, there is an increasing demand for solutions that can manage these sources’ sporadic availability. Supply and demand can be balanced by the smart grid, and excess energy can be stored for later use.
2. Demand Response
Another key application of the smart grid is demand response. This is a system that allows utilities in real-time. This information is then used to make adjustments to the power grid, and to ensure that includes everything from supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, to distribution automation systems (DAS) and advanced metering infrastructure (AMI).
3. Cybersecurity Systems
With the rise of digital technology, cybersecurity has become a critical component of the smart grid. Cybersecurity systems are used to protect against cyberattacks and data breaches, and to ensure that the smart grid remains secure and reliable.
Meta Description: Discover how the Smart Grid: Applications & Components can revolutionize the way we manage our energy consumption, reduce carbon footprint, and lower energy bills. Learn about the various applications and components of this cutting-edge technology and its potential benefits.
4. Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI):
AMI is one of the most important components of the Smart Grid. It enables energy providers to monitor energy usage in real-time, which helps them to identify peak energy demand, optimize energy distribution, and reduce energy waste. bills.AMI also lets customers keep track of how much energy they use and find places where they can use less energy and save money on their bills.
5. Demand Response (DR):
DR is a system that lets energy companies change the amount of energy they supply in real time based on how much energy people want. This system helps to prevent power outages during peak demand periods, reduce energy waste, and incentivize consumers to reduce their energy consumption during peak demand periods.
6. Energy Storage:
Energy storage is another critical component of the Smart Grid. It enables energy providers to store excess energy during off-peak periods and release it during peak demand periods, reducing the need for additional power generation. Energy storage systems can also help integrate renewable energy sources into the grid, which can be unreliable and intermittent.
7. Microgrids:
Microgrids are self-sufficient energy systems that operate independently from the main power grid. They make it possible to make, distribute, and use energy locally, which is especially helpful in remote areas or when the power goes out. Microgrids can also incorporate renewable energy sources, making them a sustainable energy solution.
8. Electric Vehicles (EVs):
EVs are becoming increasingly popular, and the Smart Grid can integrate them into the energy system to improve sustainability. The Smart Grid can provide charging stations for EVs, which can operate on renewable energy sources. EVs can also act as energy storage devices, releasing excess energy back into the grid during peak demand periods.
Potential Benefits of the Smart Grid:
The Smart Grid has several potential benefits, including:
Lower Energy Bills:
The Smart Grid enables energy providers to optimize energy distribution, reduce energy waste, and incentivize consumers to reduce their energy consumption, leading to lower energy bills for consumers.
Reduced Carbon Footprint:
The Smart Grid can integrate renewable energy sources into the grid, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions.
Improved Reliability:
The Smart Grid can identify and respond to power outages quickly, reducing downtime and improving the reliability of the energy system.
Enhanced Security:
The Smart Grid can detect and respond to cybersecurity threats quickly, protecting the energy system from malicious attacks.
Conclusion:
The Smart Grid: Applications and Components has the potential to revolutionize the way we manage our energy consumption and production, making it more efficient, reliable, and sustainable. The various components of the Smart Grid, including advanced metering infrastructure, demand response, energy storage, microgrids, and electric vehicles, work together to optimize energy distribution and reduce energy waste. The Smart Grid also has several potential benefits, including lower energy bills, a reduced carbon footprint, improved reliability, and enhanced security. As we continue to strive for a sustainable energy future, the Smart Grid is set to play a critical role in shaping the energy landscape.
FAQs:
Q: What is the Smart Grid?
A: The Smart Grid is an advanced energy management system that enables two-way communication between energy consumers and producers, making energy distribution more efficient, reliable, and sustainable.
Q: What are some applications of the Smart Grid?
A: Some applications of the Smart Grid include advanced metering infrastructure, demand response, energy storage, microgrids, and electric vehicles.
Q: What are the benefits of the Smart Grid?
A: The Smart Grid has several benefits, including lower energy bills, reduced carbon footprint, improved reliability, and enhanced security.
Q: Can the Smart Grid integrate renewable energy sources?
A: Yes, the Smart Grid can integrate renewable energy sources into the energy system, making it more sustainable and reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
Q: How can the Smart Grid help to reduce energy waste?
A: The Smart Grid can help reduce energy waste by enabling energy providers to monitor energy usage in real-time, identify peak energy demand, and adjust energy supply in response to consumer demand.

Leave a Reply